Answers section
Questions 2.10 
- For each of the following mixtures, name the most appropriate method of separation.
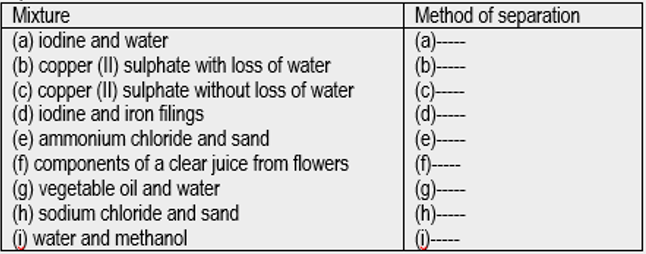
- Describe how you would separate each mixture in Question 1. Bonus Question
- The properties of certain substances A, B, C, D, and E are as given in the table that follows.

- A and E
- C and D (C is not soluble in D)
- B and C
- D and Water
- C and Water
Study the table then describe the best (easiest and cheapest) method to separate
Answers to Questions 2.10 
- For each of the following mixtures, name the best method of separation.

- Filter the mixture, and mop iodine with dry absorbent paper.
- Add the solution dropwise to a hot watch glass heated through a water bath. Water evaporates leaving copper (II) sulphate solid on the watch glass.
- Heat the solution in a distillation flask. Collect the distillate, water, in a beaker. Copper (II) sulphate remains in the distillation flask.
- Move the pole of a bar magnet over and close to the mixture. It picks iron filings, leaving iodine behind.
- Heat the mixture in a beaker, cool the emerging ammonium chloride vapour and collect it as a sublimate. Sand remains in the beaker.
- Transfer the mixture to a chromatography jar. Partially dip a chromatography paper, and allow components to rise by capillarity. Cut out coloured rings (components) from the chromatogram.
- Pour the mixture into a separating funnel clamped vertically. Open the tap to collect the water (lower) layer in a beaker and close the tap as the boundary between the two liquids reaches the tap. Open the tap and run the oil layer into the second beaker (NB: the boundary layer may need a third beaker).
- Add water to the mixture and stir to dissolve sodium chloride. Filter off the sand, wash it with fresh water, then leave it to dry. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness, losing water but retaining sodium chloride on the evaporating dish.
- Heat the mixture in a distillation flask, with fractional distillation column and thermometer in place. Collect the first distillate when the mixture is boiling but temperature is somewhat steady. Replace the container when temperature begins to rise fast and collect the second fraction, methanol.
- Use a magnet to pick out E from its mixture with A.
- Filter the mixture, collect D as a filtrate, and wash the residue, C.
- Heat the mixture. B sublimes, and C remains in the beaker.
- Carry out fractional distillation.
- Add water to the mixture and stir. Filter to obtain solid C then dry it.
