Answers section
Questions 4.2.1
- Apart from rare gases, name two gases mixed with nitrogen in the air.
- Suggest how you would remove each of the two gases named in 1 to remain with nitrogen gas.
- To remove the two gases, we need to make the air flow. Suggest two possible means by which this may be done.
- Given one large flask, conical flask, combustion tube, retort stand, trough and gas jar, draw a labelled diagram for the arrangement you would use to obtain nitrogen gas from the air.
- Give one advantage of collecting nitrogen gas by passing it through water.
- Name the impurities in the sample of nitrogen gas so prepared.
- Give two reasons why we are not so much concerned about these impurities in the sample of nitrogen gas collected.
- Write equations for the chemical reactions involving removal of the two gases named in 1.
Answers to Questions 4.2.1 
- Oxygen and carbon (IV) oxide gas
- Oxygen can be removed chemically by passing air over a heated metal, such as copper. Carbon (IV) oxide can be removed chemically by passing the air through a concentrated solution of sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide.
- Use a pump, or displace air by allowing water to flow into a bottle (an aspirator).
-
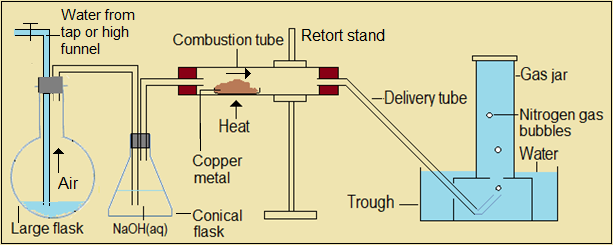
- Nitrogen gas is colourless. When we collect the gas over water, we will be able to know when the gas jar is full; that is, when the level of water has fallen below the mouth of the gas jar.
- (a) Water vapour and rare gases (or water vapour, argon, helium, xenon, krypton)
(b) Rare gases are present in very small quantities. Moreover, they are unreactive; so they do not chemically contaminate nitrogen. - NaOH(aq) + CO2(g) = NaHCO3(aq)
2Cu(s) + O2(g) = 2CuO(s)
