CHEMISTRY FORM 2
- 1.1 Structure of the atom
- 1.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number
- 1.3 Isotopes
- 1.4 Energy levels and electron arrangement
- 1.5 Development of the Periodic Table
- 1.6 Relative Atomic Mass and Isotopes
- 1.7 Ion Formation
- 1.8 Chemical Formulae
- 1.9 Chemical Equations

- 2.1 Alkali metals (Group I elements)
- 2.2 Alkali Earth Metals (Group II elements)
- 2.3 Halogens (Group VII elements)
- 2.4 Noble gases (Group VIII elements)
- 2.5 Properties and Trends Across the Periodic Table

- 3.1 Bond
- 3.2 Ionic bond
- 3.3 Giant ionic structure
- 3.4 Covalent bond
- 3.5 Co-ordinate bond
- 3.6 Molecular structures
- 3.7 Giant covalent structures
- 3.8 Metallic Bond
- 3.9 Types of bond across a period
- 3.10 Oxides of elements in Period 3
- 3.11 Chlorides of Period 3 elements

- 4.1 What is a salt?
- 4.2 Types of salt
- 4.3 Solubility of salts in water
- 4.4 Methods of preparing salts
- 4.4.1 Reacting a Metal with an Acid
- 4.4.2 Reacting an Acid with a Base (Neutralization)
- 4.4.3 Reacting an Acid with a Carbonate (or hydrogencarbonate of metal)
- 4.4.4 Combining elements Directly (Direct Combination of elements)
- 4.4.5 Precipitation (Double decomposition)
- 4.5 Action of heat on salts
- 4.6 Uses of salts

- 5.1 Electrical conduction
- 5.2 Electrical conductivity of molten substances
- 5.3 Electrical conductivity of substances in aqueous state
- 5.4 Electrolysis
- 5.5 Applications of electrolysis
- 6.1 Allotropes of carbon
- 6.2 Chemical properties of carbon
- 6.3 Carbon (IV) oxide
- 6.4 Carbon (II) oxide (CO)
- 6.5 Large scale production of sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate
- 6.6 Effect of carbon (II) oxide and carbon (IV) oxide on the environment
- 6.7 Carbon cycle

Carbon and some of its compounds: Allotropes of carbon
6.0 Carbon and some of its compounds
6.1 Allotropes of carbon
What is an allotrope?
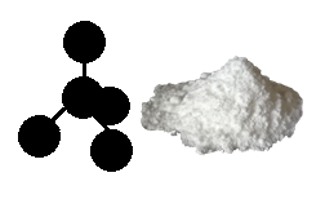
Examine the pictures in Figure 6.1.

Figure 6.1(a) Allotropes of carbon
Questions 6.1(a)
- Identify any two differences between A and B.
- If the atoms in A are identical to those in B, suggest the cause of the differences.
- The physical properties of A and B are certainly not identical. What about their chemical properties? Explain your answer.
- Suggest how you would show by chemical means that A and B are the same element, carbon.
Answers to Questions 6.1a
An element can exist in physically different forms but in the same physical state if the arrangements of atoms in them (structure) are different. But the different forms have the same chemical properties. They are called allotropes.
Allotropes are different forms of an element that exist in the same physical state.
Graphite (A) and diamond (B) are pure natural allotropes of carbon. They look quite different. But when equal amounts are burnt, they produce the same amount of carbon (IV) oxide as the only product. This confirms that they are the same element, carbon. Table 6.1 describes the two allotropes and impure forms carbon.
Table 6.1 Different forms of carbon
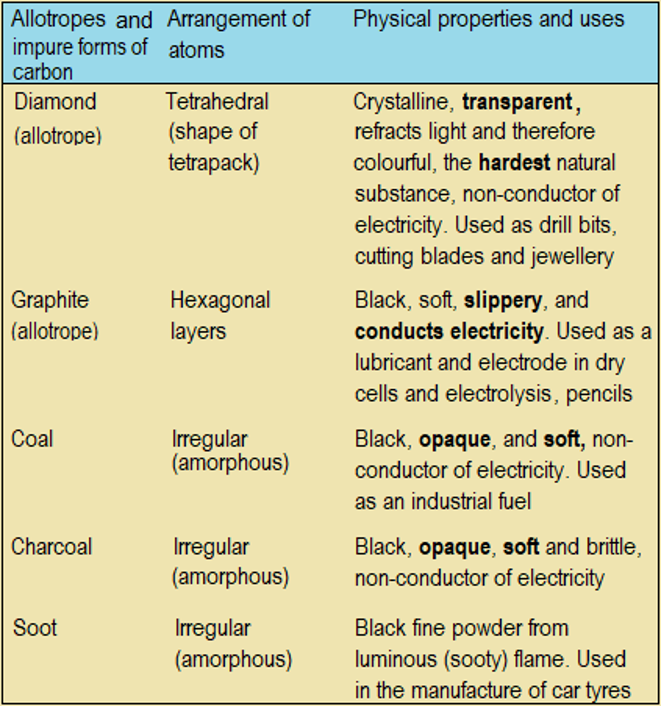

Figure 6.1(b) Structures of graphite and diamond
Questions 6.1(b)
- In what way is the structure of graphite similar to that of metals?
- In what way does the structure of graphite differ from that of metals?
- From the structure of graphite, suggest a reason why it is slippery.
- From the structure, explain why graphite conducts electricity.
- Graphite is much softer than diamond. Explain this from the structures.
- Graphite combines the properties of giant atomic and giant molecular structures. True or false? Explain your answer.
Answers to Questions 6.1b
