CHEMISTRY FORM 2
- 1.1 Structure of the atom
- 1.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number
- 1.3 Isotopes
- 1.4 Energy levels and electron arrangement
- 1.5 Development of the Periodic Table
- 1.6 Relative Atomic Mass and Isotopes
- 1.7 Ion Formation
- 1.8 Chemical Formulae
- 1.9 Chemical Equations

- 2.1 Alkali metals (Group I elements)
- 2.2 Alkali Earth Metals (Group II elements)
- 2.3 Halogens (Group VII elements)
- 2.4 Noble gases (Group VIII elements)
- 2.5 Properties and Trends Across the Periodic Table

- 3.1 Bond
- 3.2 Ionic bond
- 3.3 Giant ionic structure
- 3.4 Covalent bond
- 3.5 Co-ordinate bond
- 3.6 Molecular structures
- 3.7 Giant covalent structures
- 3.8 Metallic Bond
- 3.9 Types of bond across a period
- 3.10 Oxides of elements in Period 3
- 3.11 Chlorides of Period 3 elements

- 4.1 What is a salt?
- 4.2 Types of salt
- 4.3 Solubility of salts in water
- 4.4 Methods of preparing salts
- 4.4.1 Reacting a Metal with an Acid
- 4.4.2 Reacting an Acid with a Base (Neutralization)
- 4.4.3 Reacting an Acid with a Carbonate (or hydrogencarbonate of metal)
- 4.4.4 Combining elements Directly (Direct Combination of elements)
- 4.4.5 Precipitation (Double decomposition)
- 4.5 Action of heat on salts
- 4.6 Uses of salts

- 5.1 Electrical conduction
- 5.2 Electrical conductivity of molten substances
- 5.3 Electrical conductivity of substances in aqueous state
- 5.4 Electrolysis
- 5.5 Applications of electrolysis
- 6.1 Allotropes of carbon
- 6.2 Chemical properties of carbon
- 6.3 Carbon (IV) oxide
- 6.4 Carbon (II) oxide (CO)
- 6.5 Large scale production of sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate
- 6.6 Effect of carbon (II) oxide and carbon (IV) oxide on the environment
- 6.7 Carbon cycle

Chemical Bonding and Structure: Chlorides of Period 3 elements
3.0 Chemical Bonding and Structure
3.11 Chlorides of Period 3 elements
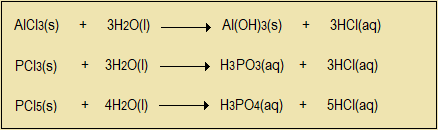
Chlorides of sodium and magnesium have giant ionic structures and are highly soluble in water. Their solutions are neutral. Dry aluminium chloride readily sublimes but is also highly soluble in water, forming an acidic solution. Chlorides of silicon and phosphorus exist as fuming solids. They too dissolve in water to form acidic solutions. Hydrogen chloride is also produced and some of it escapes as a gas.
Questions 3.11
- From the information given, what is the structure of aluminium chloride? Why?
- What does this suggest about the type of bond between chlorine and aluminium?
- Explain the fuming of chlorides of aluminium and phosphorus.
Answers to Questions 3.11
Project 3
Identify the chemical bonds and structures of as many substances around you as possible. Give reasons for your answers.
NB: In some cases, you will need to find out the chemical elements that make up the substances.
