CHEMISTRY FORM 1





- 1.1 What is matter?
- 1.2 What is Chemistry?
- 1.3 What does matter consist of?
- 1.4 Are the particles in matter stationary?
- 1.5 Arrangement, distance, and attraction between particles
- 1.6 Properties of matter (volume, shape and compression)
- 1.7 Conductors and non-conductors
- 1.8 Sources of heat
- 1.9 Bunsen burner
- 1.10 Role of Chemistry in society
- 2.1 Pure substances
- 2.2 Mixtures
- 2.3 Separation of Mixtures
- 2.4 Separation of solid-solid mixture
- 2.5 Separation of insoluble solid-liquid mixture
- 2.6 Separation of soluble solid-liquid mixture (solution)
- 2.7 Separation of immiscible liquid-liquid mixture
- 2.8 Separation of miscible liquid-liquid mixtures (solution)
- 2.9 Separation of a liquid-gas mixture
- 2.10 Selecting and using appropriate methods of separating mixtures
- 2.11 Kinetic theory of matter
- 2.12 Classification by physical states
- 2.13 Effect of heat on physical states
- 2.14 Effect of impurities on melting and boiling points
- 2.15 Permanent and non-permanent changes
- 2.16 Definitions, chemical symbols and equations
- 3.1 Simple acid-base indicators
- 3.2 Universal indicators and pH scale
- 3.3 Reactions of acids with metals
- 3.4 Reactions of acids with carbonates and hydrogen-carbonates
- 3.5 Reactions of acids with bases
- 3.6 Effects of acids on substances
- 3.7 Applications of acids and bases

- 4.1 Composition of Air
- 4.2 Fractional distillation of liquid air
- 4.3 Rusting
- 4.4 Oxygen
- 4.5 Burning of substances in air
- 4.6 Atmospheric pollution

- 5.1 Candle wax and water
- 5.2 Reactions of metals with liquid water
- 5.3 Reaction of metals with steam
- 5.4 Preparation of hydrogen gas

Acids, Bases and Indicators: Reactions of acids with metals
3.0 Acids, Bases and Indicators 
3.3 Reactions of acids with metals
How do acids react with metals?
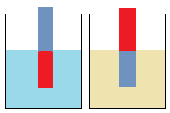
Study the set-up normally used to study reactions between metals and acids (for metals less reactive than potassium and sodium).

Open the video below, reaction of hydrochloric acid with zinc.
Caution: Drop the metal carefully not to break the test tube. It is also a good practice to wear gloves or use spatula to hold chemicals.
Questions 3.3(a)
- What is observed when the acid is added to zinc metal or vice versa?
- What is the effect of the gas on a burning splint?
- Why is the test tube collecting the gas held upside down?
- What are the elements combined in hydrochloric acid?
- The colourless solution formed contains a compound of zinc and chlorine. Name the compound.
- What is the advantage of using a transparent glass test tube?
- Write a word equation for the reaction.
Answers to Questions 3.3(a) 
The other reactive metals such as magnesium and aluminium react with acids in the same manner as zinc, producing a salt and hydrogen gas. We therefore define acid as a substance which produces hydrogen gas (and a salt) when reacted with a metal.
Questions 3.3(b)
- Complete the table below to show the substances (a) to (h) formed besides hydrogen when metals react with acids.
- Write a word equation for the reaction between aluminium and hydrochloric acid. NB: When writing an equation, the solid reactant comes first, followed by liquids then gas, whichever is there. The same applies to products.
- Potassium, and sodium metals react explosively with acids, and experiments involving them must be avoided. Otherwise they also produce salt and hydrogen gas.
- Name the salt formed when (i) sodium reacts with hydrochloric acid.
(ii) potassium reacts with sulphuric (VI) acid - Write a word equation for the reaction in (a)(i) and (a)(ii).
- Name the salt formed when (i) sodium reacts with hydrochloric acid.

NB: Extinguishing of a burning splint with a pop sound is the test for hydrogen. No other gas does the same. It is used to identify hydrogen gas.
Answers to Questions 3.3(b)
In industry
In weather and aviation, hydrogen is produced by reacting sulphuric acid with zinc metal. Hydrogen is used to fill weather balloons which fly specialized equipment to great heights as it collects weather information and sends it to the weather station.
