CHEMISTRY LEVEL 3
- 1.1 Boyle's Law
- 1.2 Charles'law
- 1.3 Combined gas law
- 1.4 Standard conditions
- 1.5 Diffusion and Graham's law
- 2.1 Relative Mass
- 2.2 Atoms, Molecules and Moles
- 2.3 Compounds and the mole
- 2.4 Empirical and Molecular formula
- 2.5 Concentration of a solution
- 2.6 Molar solutions
- 2.7 Preparation of molar solutions
- 2.8 Dilution of a solution
- 2.9 Stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- 2.10 Volumetric analysis
- 2.11 Titration
- 2.12 Redox titration
- 2.13 Atomicity and molar gas volume
- 2.14 Combining volumes of gases
- 3.1 Alkanes
- 3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
- 3.1.2 Cracking of alkanes
- 3.1.3 Nomenclature (systematic naming) of alkanes
- 3.1.4 Isomerism in alkanes
- 3.1.5 Laboratory preparation of alkanes
- 3.1.6 Physical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.8 Uses of alkanes
- 3.2 Alkenes
- 3.2.1 Nomenclature of alkenes
- 3.2.2 Isomerism in alkenes
- 3.2.3 Laboratory preparation of ethene
- 3.2.4 Physical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.5 Chemical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.6 Test for alkenes
- 3.2.7 Uses of alkenes
- 3.3 Alkynes
- 3.3.1 Nomenclature of alkynes
- 3.3.2 Isomerism in alkynes
- 3.3.3 Laboratory preparation of ethyne
- 3.3.4 Physical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.5 Chemical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.6 Test for alkynes
- 3.3.7 Uses of alkynes
- 3.4 Recommended practice of topic summary
- 4.1 Extraction of nitrogen from air
- 4.2.1 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from the air
- 4.2.2 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2)
- 4.2.3 Uses of nitrogen
- 4.3 Oxides of nitrogen
- 4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
- 4.3.2 Nitrogen (II) oxide
- 4.3.3 Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- 4.4.1 Laboratory preparation of ammonia
- 4.4.2 Solubility of ammonia in water
- 4.4.3 Reactions of aqueous ammonia (ammonia solution)
- 4.4.4 Reactions of ammonia gas
- 4.4.5 Industrial manufacture of ammonia: The Haber Process
- 4.4.6 Uses of ammonia
- 4.4.7 Nitrogenous fertilizers
- 4.5.1 Laboratory preparation of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.2 Industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.3 Reactions of dilute nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.4 Reactions of concentrated nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.5 Uses of nitric (V) acid
- 4.6.1 Action of heat on nitrates
- 4.6.2 Test for nitrates (nitrate ions, NO3-)
- 4.6.3 Air pollution by nitrogen compounds
- 4.7 Summary on nitrogen and its compounds
- 5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
- 5.1.1 Extraction of sulphur
- 5.1.2 Allotropes of sulphur
- 5.1.3 Physical properties of sulphur
- 5.1.4 Chemical properties of sulphur
- 5.2.1 Preparation of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.2 Physical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.3 Chemical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.4 Reducing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.5 Oxidization of SO2 to SO3
- 5.2.6 Oxidizing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.7 Test for sulphite (SO32-) and sulphate (SO42-) ions
- 5.2.8 Uses of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.3 Large scale (industrial) manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.1 Physical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.3 Reactions of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.4 Hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.2 Air pollution by compounds of sulphur
- 5.5 Summary on sulphur and its compounds
- 6.1 Occurrence of chlorine
- 6.2 Laboratory preparation of chlorine
- 6.3 Physical properties of chlorine
- 6.4 Chemical properties of chlorine
- 6.5 Oxidizing properties of chlorine
- 6.6 Reaction of chlorine with alkaline solutions
- 6.7 Test for chloride ions
- 6.8 Uses of chlorine and its compounds
- 6.9 Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
- 6.10 Physical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.11 Chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.12 Industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- 6.13 Uses of hydrochloric acid


Organic Chemistry 1: Formulae of alkanes
3.0 Organic Chemistry 1
3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
The first two members of the alkane family are methane, CH4 (the main component of biogas) and ethane, C2H6 (Table 3.1(a)). There are many other alkanes, with carbon atoms upto about 70 per molecule.
Table 3.1(a): Molecules of the first two alkanes

NB: Carbon and hydrogen atoms have valencies of 4 and 1 so they form 4 bonds and 1 bond respectively. This fact can be used to draw the molecule of any alkane, given the number of carbon atoms in it.
Questions 3.1(b)
- Study the two examples given in Table 3.1(a); then complete Table 3.1(b). Table 3.1(b): The first nine alkanes
- From Table 3.1(b), does the alkane in candle wax have a longer or shorter chain of carbon atoms than nonane? Explain your answer.
- From the trend (or series) in Table 3.1(b), complete the general formula CnH- of alkanes, where n is the number of carbon atoms in a molecule.
- Name the 10th member of the alkane family.
Answers to Questions 3.1(b) 
Study the arrangement of carbon atoms in butane as an example of alkanes (Figure 3.1(b)).
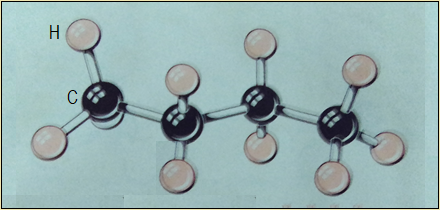
Figure 3.1(b): Ball-and-stick model of butane (an alkane)
Carbon atoms in alkanes are actually arranged in a zigzag manner, occupying the corners and ends of the zigzag. A simple skeletal formula (representation) of alkanes is therefore as shown in Figure 3.1(c).

Figure 3.1(c): Arrangement of carbon atoms in open chain alkanes
The main source of alkanes is crude oil, which is a solution of many different oils.
Questions 3.1(c)
- Name a suitable method of separating components of crude oil.
- What does this method of separation rely on?
Answers to Questions 3.1(c) 
Observe the following animation on separation of components of crude oil.
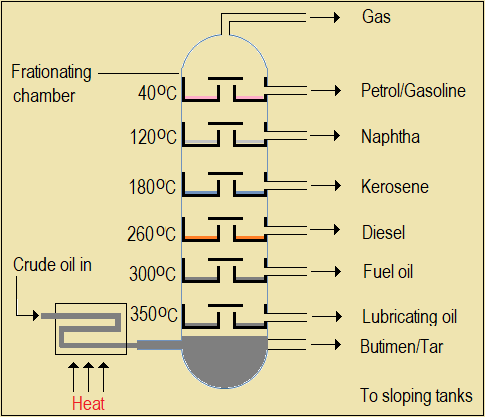
Figure 3.1(d): Animate a hot flame and vapours of the different colours shown, rising and condensing in the trays
Questions 3.1(d)
In the animation, identify the component with (a) the lowest and (b) highest boiling point.
Answers to Questions 3.1(d) 
