CHEMISTRY LEVEL 3
- 1.1 Boyle's Law
- 1.2 Charles'law
- 1.3 Combined gas law
- 1.4 Standard conditions
- 1.5 Diffusion and Graham's law
- 2.1 Relative Mass
- 2.2 Atoms, Molecules and Moles
- 2.3 Compounds and the mole
- 2.4 Empirical and Molecular formula
- 2.5 Concentration of a solution
- 2.6 Molar solutions
- 2.7 Preparation of molar solutions
- 2.8 Dilution of a solution
- 2.9 Stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- 2.10 Volumetric analysis
- 2.11 Titration
- 2.12 Redox titration
- 2.13 Atomicity and molar gas volume
- 2.14 Combining volumes of gases
- 3.1 Alkanes
- 3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
- 3.1.2 Cracking of alkanes
- 3.1.3 Nomenclature (systematic naming) of alkanes
- 3.1.4 Isomerism in alkanes
- 3.1.5 Laboratory preparation of alkanes
- 3.1.6 Physical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.8 Uses of alkanes
- 3.2 Alkenes
- 3.2.1 Nomenclature of alkenes
- 3.2.2 Isomerism in alkenes
- 3.2.3 Laboratory preparation of ethene
- 3.2.4 Physical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.5 Chemical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.6 Test for alkenes
- 3.2.7 Uses of alkenes
- 3.3 Alkynes
- 3.3.1 Nomenclature of alkynes
- 3.3.2 Isomerism in alkynes
- 3.3.3 Laboratory preparation of ethyne
- 3.3.4 Physical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.5 Chemical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.6 Test for alkynes
- 3.3.7 Uses of alkynes
- 3.4 Recommended practice of topic summary
- 4.1 Extraction of nitrogen from air
- 4.2.1 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from the air
- 4.2.2 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from ammonium nitrite (NH4NO2)
- 4.2.3 Uses of nitrogen
- 4.3 Oxides of nitrogen
- 4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
- 4.3.2 Nitrogen (II) oxide
- 4.3.3 Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- 4.4.1 Laboratory preparation of ammonia
- 4.4.2 Solubility of ammonia in water
- 4.4.3 Reactions of aqueous ammonia (ammonia solution)
- 4.4.4 Reactions of ammonia gas
- 4.4.5 Industrial manufacture of ammonia: The Haber Process
- 4.4.6 Uses of ammonia
- 4.4.7 Nitrogenous fertilizers
- 4.5.1 Laboratory preparation of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.2 Industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.3 Reactions of dilute nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.4 Reactions of concentrated nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.5 Uses of nitric (V) acid
- 4.6.1 Action of heat on nitrates
- 4.6.2 Test for nitrates (nitrate ions, NO3-)
- 4.6.3 Air pollution by nitrogen compounds
- 4.7 Summary on nitrogen and its compounds
- 5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
- 5.1.1 Extraction of sulphur
- 5.1.2 Allotropes of sulphur
- 5.1.3 Physical properties of sulphur
- 5.1.4 Chemical properties of sulphur
- 5.2.1 Preparation of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.2 Physical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.3 Chemical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.4 Reducing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.5 Oxidization of SO2 to SO3
- 5.2.6 Oxidizing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.7 Test for sulphite (SO32-) and sulphate (SO42-) ions
- 5.2.8 Uses of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.3 Large scale (industrial) manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.1 Physical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.3 Reactions of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.4 Hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.2 Air pollution by compounds of sulphur
- 5.5 Summary on sulphur and its compounds
- 6.1 Occurrence of chlorine
- 6.2 Laboratory preparation of chlorine
- 6.3 Physical properties of chlorine
- 6.4 Chemical properties of chlorine
- 6.5 Oxidizing properties of chlorine
- 6.6 Reaction of chlorine with alkaline solutions
- 6.7 Test for chloride ions
- 6.8 Uses of chlorine and its compounds
- 6.9 Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
- 6.10 Physical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.11 Chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.12 Industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- 6.13 Uses of hydrochloric acid


Organic Chemistry 1: Chemical properties of alkanes
3.0 Organic Chemistry 1
3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
Watch the video of burning candle, kerosene and cooking gas.

Figure 3.1(a): Some common alkanes in use (candle wax, kerosene, and cooking gas)
(courtesy Youtube-In which physical state do alkanes burn or react by ormalearn)
Questions 3.1.7(a)
- Identify (a) one product of incomplete combustion of alkanes, and (b) two products of complete combustion of alkanes.
- Write an equation for the complete burning of (a) methane and (b) butane in air.
- Study the burning of candle wax and kerosene keenly. Do alkanes burn as liquids or in gaseous state? Explain your answer.
Answers to Questions 3.1.7(a) 
Alkanes burn in air (oxygen) to form steam and carbon (IV) oxide. They do so in gaseous state only.
Reaction with halogens (substitution reactions)
- Prepare methane and pass it into a jar full of chlorine gas. Take observations.
- Repeat the procedure using bromine, then iodine vapour in place of chlorine gas.
NB: Light (ultraviolet) is required for these reactions.
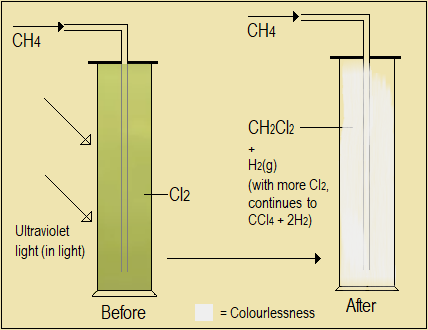
Figure 3.1.7: Reaction of alkanes with chlorine and other halogens
Questions 3.1.7(b)
- State the observable change when methane is mixed with chlorine gas in diffused sunlight (in the room).
- Suggest the role of sunlight in this reaction.
- During the reaction, each chlorine molecule splits into single atoms which are unstable (like in many other reactions). Then one
chlorine atom knocks off and substitutes (replaces) one hydrogen atom from methane, in a process called substitution reaction.
- What do you expect to happen to the other chlorine atom and the hydrogen atom substituted? Explain.
- Write the formulae of the two products at this stage.
- Write the equation for the reaction at this stage. Remember to write ultraviolet light over the arrow in the equation.
- Substitution reaction continues in stages till all the four hydrogen atoms in methane are replaced by chlorine atoms. Complete the following equations for the substitution reaction.
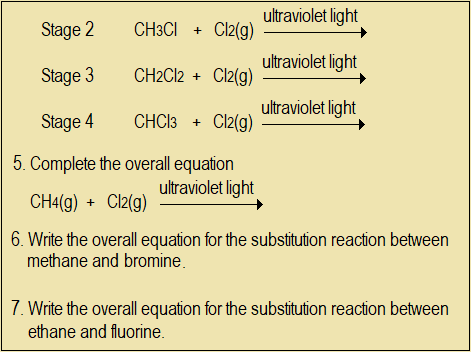
Answers to Questions 3.1.7b 
Alkanes undergo substitution reactions with halogens but only in presence of light (ultraviolet). The colours of halogens are lost in the process.
The products are called haloalkanes, because they are compounds of halogens and alkanes. Examples are chloromethane (CH3Cl), bromomethane (CH3Br), iodomethane (CH3I) and fluoromethane (CH3F).
IUPAC naming system applies to haloalkanes as well. We first identify the longest chain containing the carbon to which a halogen is attached. Numbering begins with the carbon atom closest to or attached to the halogen.
Examples
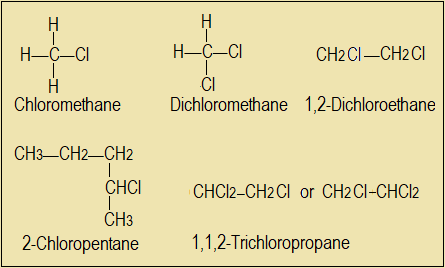
Questions 3.1.7(c)
Name the following halo-alkanes according to the IUPAC nomenclature.
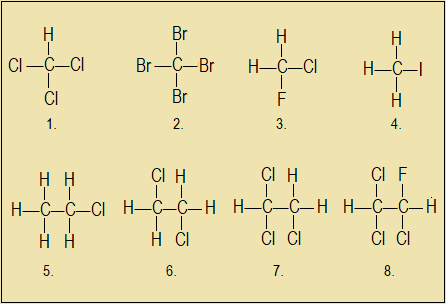
Answers to Questions 3.1.7c 
