CHEMISTRY LEVEL 3
- 1.1 Boyle's Law
- 1.2 Charles'law
- 1.3 Combined gas law
- 1.4 Standard conditions
- 1.5 Diffusion and Graham's law
- 2.1 Relative Mass
- 2.2 Atoms, Molecules and Moles
- 2.3 Compounds and the mole
- 2.4 Empirical and Molecular formula
- 2.5 Concentration of a solution
- 2.6 Molar solutions
- 2.7 Preparation of molar solutions
- 2.8 Dilution of a solution
- 2.9 Stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- 2.10 Volumetric analysis
- 2.11 Titration
- 2.12 Redox titration
- 2.13 Atomicity and molar gas volume
- 2.14 Combining volumes of gases
- 3.1 Alkanes
- 3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
- 3.1.2 Cracking of alkanes
- 3.1.3 Nomenclature (systematic naming) of alkanes
- 3.1.4 Isomerism in alkanes
- 3.1.5 Laboratory preparation of alkanes
- 3.1.6 Physical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.8 Uses of alkanes
- 3.2 Alkenes
- 3.2.1 Nomenclature of alkenes
- 3.2.2 Isomerism in alkenes
- 3.2.3 Laboratory preparation of ethene
- 3.2.4 Physical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.5 Chemical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.6 Test for alkenes
- 3.2.7 Uses of alkenes
- 3.3 Alkynes
- 3.3.1 Nomenclature of alkynes
- 3.3.2 Isomerism in alkynes
- 3.3.3 Laboratory preparation of ethyne
- 3.3.4 Physical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.5 Chemical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.6 Test for alkynes
- 3.3.7 Uses of alkynes
- 3.4 Recommended practice of topic summary
- 4.1 Extraction of nitrogen from air
- 4.2.1 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from the air
- 4.2.2 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from ammonium nitrite ((NH4NO2))
- 4.2.3 Uses of nitrogen
- 4.3 Oxides of nitrogen
- 4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
- 4.3.2 Nitrogen (II) oxide
- 4.3.3 Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- 4.4.1 Laboratory preparation of ammonia
- 4.4.2 Solubility of ammonia in water
- 4.4.3 Reactions of aqueous ammonia (ammonia solution)
- 4.4.4 Reactions of ammonia gas
- 4.4.5 Industrial manufacture of ammonia: The Haber Process
- 4.4.6 Uses of ammonia
- 4.4.7 Nitrogenous fertilizers
- 4.5.1 Laboratory preparation of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.2 Industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.3 Reactions of dilute nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.4 Reactions of concentrated nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.5 Uses of nitric (V) acid
- 4.6.1 Action of heat on nitrates
- 4.6.2 Test for nitrates (nitrate ions, NO3-)
- 4.6.3 Air pollution by nitrogen compounds
- 4.7 Summary on nitrogen and its compounds
- 5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
- 5.1.1 Extraction of sulphur
- 5.1.2 Allotropes of sulphur
- 5.1.3 Physical properties of sulphur
- 5.1.4 Chemical properties of sulphur
- 5.2.1 Preparation of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.2 Physical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.3 Chemical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.4 Reducing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.5 Oxidization of SO2 to SO3
- 5.2.6 Oxidizing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.7 Test for sulphite (SO32-) and sulphate (SO42-) ions
- 5.2.8 Uses of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.3 Large scale (industrial) manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.1 Physical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.3 Reactions of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.4 Hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.2 Air pollution by compounds of sulphur
- 5.5 Summary on sulphur and its compounds
- 6.1 Occurrence of chlorine
- 6.2 Laboratory preparation of chlorine
- 6.3 Physical properties of chlorine
- 6.4 Chemical properties of chlorine
- 6.5 Oxidizing properties of chlorine
- 6.6 Reaction of chlorine with alkaline solutions
- 6.7 Test for chloride ions
- 6.8 Uses of chlorine and its compounds
- 6.9 Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
- 6.10 Physical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.11 Chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.12 Industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- 6.13 Uses of hydrochloric acid


Sulphur and its Compounds: Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
Oxidation
Sulphuric (VI) acid is obtained from sulphur. Can the acid react with sulphur, "destroying" what produces it? What about magnesium, and even copper which is below hydrogen in the reactivity series? Observe the video demonstration besides Figure 5.3.2(a).

Figure 5.3.2(a): Reactions of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
Questions 5.3.2(a)
- State and explain, using chemical equations, the observations in each of the four demonstrations (with sulphur, copper, magnesium, and carbon).
- Complete the following general word equations for the oxidation of elements by concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid.
- Metal + Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- Non-metal + Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- Give three reasons why concentrated sulphuric (VI) is exceptionally corrosive, attacking metals and non-metals alike.
- Which other acid behaves in a similar way as concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid?
Answers to Questions 5.3.2(a) 
Dehydration
Watch the video demonstration on the dehydration of cane sugar (C12H22O11) by concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid; then study the pictures in Figure 5.3.2(b).
(courtesy Youtube-Reaction of sugar with concentrated sulfuric acid by Alex)

Figure 5.3.2(b): Dehydration of cane sugar by concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid with cane sugar https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L0Pl1iGjct4
- Hydrated copper (II) sulphate (CuSO4.5H2O)
- Cane sugar (C12H22O11)
- Ethanol (C2H5OH or CH3CH2OH)
- Methanoic acid (HCOOH)
- Wood or paper, -(C6H10O5)-n
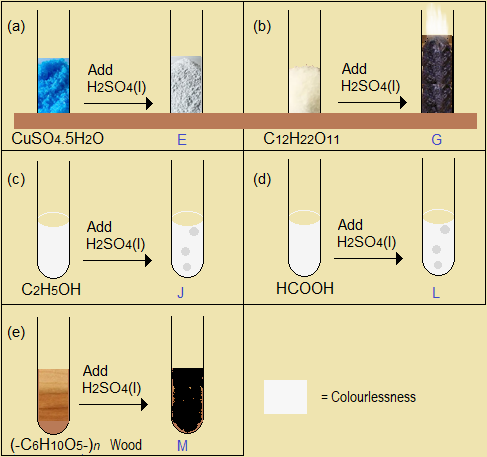
Figure 5.3.2(c): Dehydrating property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
In dehydration, concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid removes elements of water (H and O) as complete water molecules, nH2O, where n is a whole number. The acid itself remains intact as H2SO4.
Questions 5.3.2(b)
- Write the formula and name of each of the products of dehydration Solid G, Gas J, Gas L, Solid M.
- Write a complete equation for each of the dehydration reactions (b) to (e) represented in Figure 5.3.2(c). Part (a) is already done below as an example.
- Identify what looks like white fumes in Figure 5.3.2(b), and explain why it is so thick.
- As shown in Figure 5.3.2(c) and the video, a relatively small amount of cane sugar produces a "large quantity" of black solid. Suggest an explanation for this.
- Explain why concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid is highly corrosive.
- Prepare a brief summary of the oxidation and dehydrating properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid.
CuSO4.5H2O(s) H2SO4(l)→ CuSO4(s) + 5H2O(l)
Answers to Questions 5.3.2(b) 
Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid has a high affinity for elements of water. It therefore dehydrates and burns virtually all organic materials such as wood, paper, flesh, and cane sugar, charring them first to charcoal, and further to carbon (IV) oxide.
