×








CHEMISTRY LEVEL 3
1. GAS LAWS
- 1.1 Boyle's Law
- 1.2 Charles'law
- 1.3 Combined gas law
- 1.4 Standard conditions
- 1.5 Diffusion and Graham's law
2. THE MOLE: Formulae and Chemical Equations
- 2.1 Relative Mass
- 2.2 Atoms, Molecules and Moles
- 2.3 Compounds and the mole
- 2.4 Empirical and Molecular formula
- 2.5 Concentration of a solution
- 2.6 Molar solutions
- 2.7 Preparation of molar solutions
- 2.8 Dilution of a solution
- 2.9 Stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- 2.10 Volumetric analysis
- 2.11 Titration
- 2.12 Redox titration
- 2.13 Atomicity and molar gas volume
- 2.14 Combining volumes of gases
3. ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1
- 3.1 Alkanes
- 3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
- 3.1.2 Cracking of alkanes
- 3.1.3 Nomenclature (systematic naming) of alkanes
- 3.1.4 Isomerism in alkanes
- 3.1.5 Laboratory preparation of alkanes
- 3.1.6 Physical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.8 Uses of alkanes
- 3.2 Alkenes
- 3.2.1 Nomenclature of alkenes
- 3.2.2 Isomerism in alkenes
- 3.2.3 Laboratory preparation of ethene
- 3.2.4 Physical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.5 Chemical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.6 Test for alkenes
- 3.2.7 Uses of alkenes
- 3.3 Alkynes
- 3.3.1 Nomenclature of alkynes
- 3.3.2 Isomerism in alkynes
- 3.3.3 Laboratory preparation of ethyne
- 3.3.4 Physical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.5 Chemical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.6 Test for alkynes
- 3.3.7 Uses of alkynes
- 3.4 Recommended practice of topic summary
4. NITROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS
- 4.1 Extraction of nitrogen from air
- 4.2.1 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from the air
- 4.2.2 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from ammonium nitrite ((NH4NO2))
- 4.2.3 Uses of nitrogen
- 4.3 Oxides of nitrogen
- 4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
- 4.3.2 Nitrogen (II) oxide
- 4.3.3 Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- 4.4.1 Laboratory preparation of ammonia
- 4.4.2 Solubility of ammonia in water
- 4.4.3 Reactions of aqueous ammonia (ammonia solution)
- 4.4.4 Reactions of ammonia gas
- 4.4.5 Industrial manufacture of ammonia: The Haber Process
- 4.4.6 Uses of ammonia
- 4.4.7 Nitrogenous fertilizers
- 4.5.1 Laboratory preparation of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.2 Industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.3 Reactions of dilute nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.4 Reactions of concentrated nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.5 Uses of nitric (V) acid
- 4.6.1 Action of heat on nitrates
- 4.6.2 Test for nitrates (nitrate ions, NO3-)
- 4.6.3 Air pollution by nitrogen compounds
- 4.7 Summary on nitrogen and its compounds
5. SULPHUR AND ITS COMPOUNDS
- 5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
- 5.1.1 Extraction of sulphur
- 5.1.2 Allotropes of sulphur
- 5.1.3 Physical properties of sulphur
- 5.1.4 Chemical properties of sulphur
- 5.2.1 Preparation of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.2 Physical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.3 Chemical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.4 Reducing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.5 Oxidization of SO2 to SO3
- 5.2.6 Oxidizing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.7 Test for sulphite (SO32-) and sulphate (SO42-) ions
- 5.2.8 Uses of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.3 Large scale (industrial) manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.1 Physical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.3 Reactions of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.4 Hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.2 Air pollution by compounds of sulphur
- 5.5 Summary on sulphur and its compounds
6. CHLORINE AND ITS COMPOUNDS
- 6.1 Occurrence of chlorine
- 6.2 Laboratory preparation of chlorine
- 6.3 Physical properties of chlorine
- 6.4 Chemical properties of chlorine
- 6.5 Oxidizing properties of chlorine
- 6.6 Reaction of chlorine with alkaline solutions
- 6.7 Test for chloride ions
- 6.8 Uses of chlorine and its compounds
- 6.9 Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
- 6.10 Physical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.11 Chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.12 Industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- 6.13 Uses of hydrochloric acid
7. A guide to chemical tests based on this module

Content developer

Nitrogen and its Compounds: Nitrogen (I) oxide
4.0 Nitrogen and its Compounds
4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
Nitrogen (I) oxide is prepared in the laboratory by thermally decomposing (heating) fresh solid ammonium nitrate.
NB: On a smaller scale, boiling tubes may be used in place of the flask and gas jar.
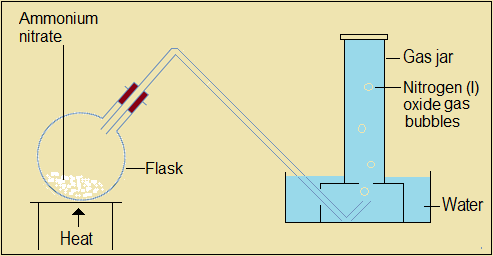
Figure 4.3.1(a):Set-up to prepare nitrogen (I) oxide from freshly prepared ammonium nitrite
Observe the video demonstration of preparation and properties of nitrogen (I) oxide, alongside Figure 4.3.1(b):
Questions 4.3.1
- Write the chemical formula of ammonium nitrate.
- Write the chemical formula of nitrogen (I) oxide (oxygen has a valency of 2 in all its compounds).
- Suggest the name and chemical formula of the other product accompanying nitrogen (I) oxide.
- Write an equation for the thermal decomposition of ammonium nitrate to produce nitrogen (I) oxide.
- What is the indication that nitrogen (I) oxide is insoluble in water?
- How would you obtain a dry sample of nitrogen (I) oxide (Hint: N = 14; O = 16)? Explain your selected method of collection.
- State four physical properties of nitrogen (I) oxide.
- State three chemical properties of nitrogen (I) oxide.
- Write equations for the reactions of nitrogen (I) oxide with each of the following substances. (a) heated copper metal (b) burning sulphur
- Complete the general equation, Element + Nitrogen (I) oxide →
- Explain how you would distinguish nitrogen (I) oxide from oxygen gas by physical means.
- State two uses of nitrogen (I) oxide.

Figure 4.3.1(b): Illustrating some properties of nitrogen (I) oxide (N2O)
Answers to Questions 4.3.1 
