CHEMISTRY LEVEL 3
- 1.1 Boyle's Law
- 1.2 Charles'law
- 1.3 Combined gas law
- 1.4 Standard conditions
- 1.5 Diffusion and Graham's law
- 2.1 Relative Mass
- 2.2 Atoms, Molecules and Moles
- 2.3 Compounds and the mole
- 2.4 Empirical and Molecular formula
- 2.5 Concentration of a solution
- 2.6 Molar solutions
- 2.7 Preparation of molar solutions
- 2.8 Dilution of a solution
- 2.9 Stoichiometry of chemical reactions
- 2.10 Volumetric analysis
- 2.11 Titration
- 2.12 Redox titration
- 2.13 Atomicity and molar gas volume
- 2.14 Combining volumes of gases
- 3.1 Alkanes
- 3.1.1 Formulae of alkanes
- 3.1.2 Cracking of alkanes
- 3.1.3 Nomenclature (systematic naming) of alkanes
- 3.1.4 Isomerism in alkanes
- 3.1.5 Laboratory preparation of alkanes
- 3.1.6 Physical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.7 Chemical properties of alkanes
- 3.1.8 Uses of alkanes
- 3.2 Alkenes
- 3.2.1 Nomenclature of alkenes
- 3.2.2 Isomerism in alkenes
- 3.2.3 Laboratory preparation of ethene
- 3.2.4 Physical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.5 Chemical properties of alkenes
- 3.2.6 Test for alkenes
- 3.2.7 Uses of alkenes
- 3.3 Alkynes
- 3.3.1 Nomenclature of alkynes
- 3.3.2 Isomerism in alkynes
- 3.3.3 Laboratory preparation of ethyne
- 3.3.4 Physical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.5 Chemical properties of alkynes
- 3.3.6 Test for alkynes
- 3.3.7 Uses of alkynes
- 3.4 Recommended practice of topic summary
- 4.1 Extraction of nitrogen from air
- 4.2.1 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from the air
- 4.2.2 Laboratory preparation of nitrogen gas from ammonium nitrite ((NH4NO2))
- 4.2.3 Uses of nitrogen
- 4.3 Oxides of nitrogen
- 4.3.1 Nitrogen (I) oxide
- 4.3.2 Nitrogen (II) oxide
- 4.3.3 Nitrogen (IV) oxide
- 4.4.1 Laboratory preparation of ammonia
- 4.4.2 Solubility of ammonia in water
- 4.4.3 Reactions of aqueous ammonia (ammonia solution)
- 4.4.4 Reactions of ammonia gas
- 4.4.5 Industrial manufacture of ammonia: The Haber Process
- 4.4.6 Uses of ammonia
- 4.4.7 Nitrogenous fertilizers
- 4.5.1 Laboratory preparation of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.2 Industrial manufacture of nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.3 Reactions of dilute nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.4 Reactions of concentrated nitric (V) acid
- 4.5.5 Uses of nitric (V) acid
- 4.6.1 Action of heat on nitrates
- 4.6.2 Test for nitrates (nitrate ions, NO3-)
- 4.6.3 Air pollution by nitrogen compounds
- 4.7 Summary on nitrogen and its compounds
- 5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
- 5.1.1 Extraction of sulphur
- 5.1.2 Allotropes of sulphur
- 5.1.3 Physical properties of sulphur
- 5.1.4 Chemical properties of sulphur
- 5.2.1 Preparation of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.2 Physical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.3 Chemical properties of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.4 Reducing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.5 Oxidization of SO2 to SO3
- 5.2.6 Oxidizing action of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.2.7 Test for sulphite (SO32-) and sulphate (SO42-) ions
- 5.2.8 Uses of sulphur (IV) oxide
- 5.3 Large scale (industrial) manufacture of sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.1 Physical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.2 Chemical properties of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.3.3 Reactions of dilute sulphuric (VI) acid
- 5.4 Hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
- 5.4.2 Air pollution by compounds of sulphur
- 5.5 Summary on sulphur and its compounds
- 6.1 Occurrence of chlorine
- 6.2 Laboratory preparation of chlorine
- 6.3 Physical properties of chlorine
- 6.4 Chemical properties of chlorine
- 6.5 Oxidizing properties of chlorine
- 6.6 Reaction of chlorine with alkaline solutions
- 6.7 Test for chloride ions
- 6.8 Uses of chlorine and its compounds
- 6.9 Preparation of hydrogen chloride gas
- 6.10 Physical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.11 Chemical properties of hydrogen chloride
- 6.12 Industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- 6.13 Uses of hydrochloric acid


Sulphur and its Compounds: Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
5.0 Sulphur and its Compounds
5.4.1 Chemical properties of hydrogen sulphide
Reaction with water
H2S(g) + H2O(l) → H2S(aq)
Questions 5.4.1(a)
- From the demonstration, state with reason whether hydrogen sulphide is acidic or basic.
- What is the evidence that hydrogen sulphide reacts with water?
Answers to Questions 5.4.1(a) 
Combustion in air
Observe the video demonstration of combustion of hydrogen sulphide in air, and the accompanying pictures in Figure 5.4.1(b).
| Condition | Observations when hydrogen sulphide is burning in oxygen (or air) |
| Limited supply of oxygen | 
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/earth-and-planetary-sciences/hydrogen-sulphide |
| Excess oxygen | Insert diagram |
Figure 5.4.1(b): Combustion of hydrogen sulphide in air
Questions 5.4.1(b)
Complete the following table to describe, in words and chemical equations, the burning of hydrogen sulphide in air.
| Condition | Observations when hydrogen sulphide is burning in oxygen (or air) | Equation for the reaction |
| Limited supply of oxygen | ||
| Excess oxygen |
Answers to Questions 5.4.1(b) 
Reducing property of hydrogen sulphide
Observe the video demonstration of reducing property of hydrogen sulphide, and the accompanying pictures in Figure 5.4.1(c).
(courtesy Youtube-Reducing Agents: Preparation and Tests for SO2 and H2S. by FranklyChemistry)
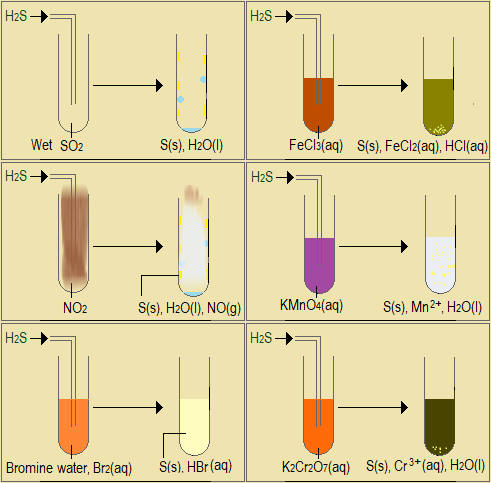
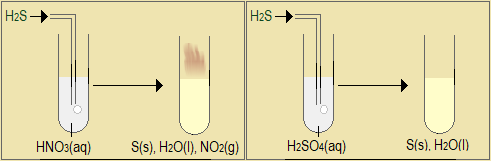
Figure 5.4.1(c): Reducing property of hydrogen sulphide
Questions 5.4.1(c)
- Complete the following table to describe, in words and chemical equations, the reducing property of hydrogen sulphide.
Substance Observations when hydrogen sulphide is reacted with the substance Equation for the reaction SO2(g) NO2(g) Br2(aq) FeCl3(aq) KMnO4(aq) K2Cr2O7(aq) H2O2(aq) HNO3(aq) H2SO4(aq) - State the common observation in all these demonstrations, neglecting the acids.
Answers to Questions 5.4.1(c) 
Precipitation of metallic ions
Observe the video demonstration of precipitation of metallic ions by hydrogen sulphide, and the accompanying pictures in Figure 5.4.1(d).
(courtesy Youtube-Sulphur and its Compounds:-Properties of Hydrogen Sulphide-11 by OAKS - Your Personalised Learning Companion)
| Metallic ions | Observations when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled through a solution of the metallic ions |
| Cu2+ | 
|
| Pb2+ | 
|
| Fe2+ | 
|
| Zn2+ | 
|
Questions 5.4.1(d)
- Complete the following table to describe, in words and chemical equations, the precipitation of metallic ions by hydrogen sulphide. Hint: The gas first dissolves in water to produce sulphide ions (S2-) and hydrogen ions, H+ (which remains in solution).
Metallic ions Observations when hydrogen sulphide is bubbled through a solution of the ions Equation for the reaction Cu2+(aq) Pb2+(aq) Fe2+(aq) Zn2+(aq) - Metal sulphides are salts. (a) Write a general conclusion about the solubility of metal sulphides. (b) Suggest three possible exceptions to your conclusion in (a).
- Explain why the reactions with metallic ions are considered as precipitation and not reduction reactions (Hint: Are there ions in the solid metal sulphides?)
-
- Although hydrogen sulphide precipitates other metallic ions, only precipitation of lead (II) ions is used as a confirmatory test for the gas. Explain.
- Identify one other compound of lead that may be used as an alternative to lead acetate, in testing for hydrogen sulphide. Explain your choice.
- Name two of the substances that could be responsible for the blackness of waste and sewage water.
Answers to Questions 5.4.1(d) 
